|
|
|
Back to |
Running
With QUERY, you can run a query manually or you can perform unattended data downloads by scheduling runs for off-peak hours to reduce system resource load. For unattended data downloads, if you provide an e-mail address, QUERY can send e-mail notification or an attached copy of the results file when the run finishes.
Before you run a large query. It is recommended that you first do a test run with a few hundred records. Once you are satisfied with the test run, you can proceed with your query.
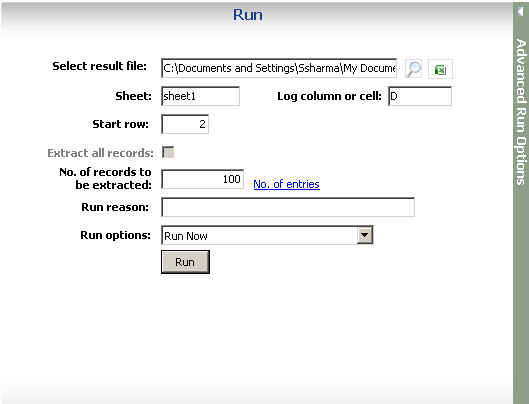
The Run pane with an Excel file open.
The Run pane contains the following options:
Select Result file or database |
Specify a result file or database. The default is the file or database that you saved during the mapping step. |
Sheet, Table (Excel, Access) |
The sheet or table to which the data is sent. The default is the sheet or table that you specified during the mapping step. However, you can specify another sheet or table. |
Record delimiter (text files only) |
The character used to separate the values of each row of data. Select from |, ;, #, $, &, @, %, ,, _, *, ', and TAB. |
Header delimiter (text files only) |
The character used to separate the values in each header row. Select from |, ;, #, $, &, @, %, ,, _, *, ', and TAB. |
Start row |
Specify the row wherein you want QUERY to begin adding records. (Available only for Excel files.) |
Log Column/Cell (Excel files) and Log Column (Access tables) |
Specify the column and cell or column in which SAP log information is written. This information appears automatically.
|
Extract all records check box |
Select this check box if you do not know how many records are available for the download. Selecting this check box has the same effect as if No. of records to extract is set to '0'. Must be enabled by the administrator. |
No. of records to extract |
Specify how many records should be extracted. If '0' is specified, QUERY returns all records (if allowed by the administrator) or the maximum number of records that you can download. The default is 1 million records, which is set by the administrator. If you specify a number that exceeds the maximum limit, the query will not run. The Extract all records setting overrides this setting. |
Run reason |
Add a comment about why the query was run. |
Run options |
Select Run now or Run later to specify an unattended run. |
To run a query
- In the Run pane, click Run.
For Excel files, the file opens and the results are displayed.
In Excel 2007, each cell can accommodate 8192 characters and in Excel 2003 each cell can accommodate 1024 characters. If a long text field that was used in the query contains characters that exceed these limits, the field must be trimmed to ensure a successful download.
Adding run time values
If you have included variables as criteria values, at run time you need to add other values or add the name of the file that contains the values.
- If you have included variables run time variables as criteria values, at run time you need to add other values or add the name of the file that contains the values input them.
- If values were set as "Required" when the criteria were set, it is mandatory to provide inputs.
- If you used the IN operator, you can select an Excel or a text file.
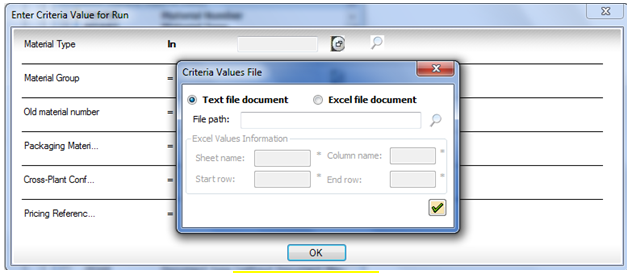
The Criteria Values File dialog box with the Text File option selected.
For an Excel file, specify the following required settings:
- Sheet Name
- Column Name
- Start Row
- End Row
For a text file, you need only specify the path for the file that contains the values.
Scheduling a run
With QUERY, you can schedule unattended queries.
To schedule a run
- Under Run options, click Run later, and then click Run. You are prompted to save the query.
The Schedule Run wizard appears. Follow the steps to schedule a query run.
To complete the Schedule Run Wizard
- Do one of the following:
- Click Capture SAP details to automatically retrieve the information that is selected on the SAP Logon dialog box. Clicking Capture is the easiest and most error-free method for adding logon details to the scheduler.
-or-
- Type in the required information in the fields.
SAP System Name |
Specify the SAP system name |
Application Server Host |
Enter the host name. |
System number |
Specify the system number. |
Use Logon Group |
Select this check box to update logon group information. |
Logon Group |
If available, type the auto logon group information. |
Message Server Host |
If available, type the message server host information. |
Use SSO1 |
Select this check box to enable single sign on. With single sign on, the SAP system uses the Windows credentials (user name and password) for each user. |
Partner |
Specify this connection parameter if you select single sign on. |
Client |
Enter the client number. |
User name |
Specify the user name. |
Password |
Specify the SAP password for the user. |
Language |
Specify the language that the system should use. |
EP URL |
If available, specify the enterprise portal URL. |
E-mail notification |
Type the e-mail address for the person who you want to receive notification by e-mail message when the scheduled run is completed. You can specify multiple e-mail addresses that are separated by semicolon. |
Attach data file to the mail |
Select to attach the results file to the e-mail message. |
Run on console |
If the query is to be run from the command line, select Run on console. |
- Click Test to confirm that your logon information works. Click Next.
- On page 2, for Excel, text, and XML files, and for Access tables, select one:
Perform this task: |
Once: Schedules a one-time run. If you select Once, you can set the Run on date. Daily: Schedules a daily run. Weekly: Schedules a weekly run. If you select Schedule Weekly, enter the weekly frequency. You can also specify the day of the week for the run. Monthly: Schedules a monthly run. If you select Schedule Monthly, enter either the date each month for the run or the ordinal date. You also mark the months for the run. |
Run as |
If you want the task to run even if you are not logged on, enter your Windows user name. |
Start Time |
Select the time of day when the scheduled task is to take place. |
Password |
Enter the password the user provides to log onto Windows. |
Run only if logged on |
When selected, the user must be logged on for the scheduled task to be completed. |
The Scheduler pane
In the Scheduler pane you can manage all your scheduled queries. View the query name, the name of the output (data) file, the time when the run is scheduled, the last date and time when the query was run, the next time the query is scheduled to run, and the e-mail address of the person who will receive notification that the query has run. You can also set the schedule for queries.
To open the Scheduler pane
- On the Tools tab
 , click Scheduler
, click Scheduler  .
.
To edit a schedule
- Click Edit
 to open the Schedule Run Wizard to edit options.
to open the Schedule Run Wizard to edit options.
To remove a query from the schedule queue
- Click Delete
 .
.
To schedule a run from the Scheduler pane
- Click Schedule a run
 . The Schedule Run Wizard opens.
. The Schedule Run Wizard opens.
Stopping a query run
You can stop a running query by clicking the Stop button ![]() . The stop functionality is useful if you inadvertently begin a large run or if a runaway process is impacting database performance.
. The stop functionality is useful if you inadvertently begin a large run or if a runaway process is impacting database performance.
Note: You can stop a running query, only if it has been created with tables as the data source. You cannot stop a query run that contains InfoSets, SAP queries, or logical databases.
|
Also in this section Publishing macros in an Excel workbook |

 Home
Home Back
Back Forward
Forward Contents
Contents Index
Index Product Help
Product Help Support
Support Print
Print Feedback
Feedback Trademarks
Trademarks Back to top
Back to top


