| diagram |
 |
| namespace |
http://www.opengis.net/gml |
| type |
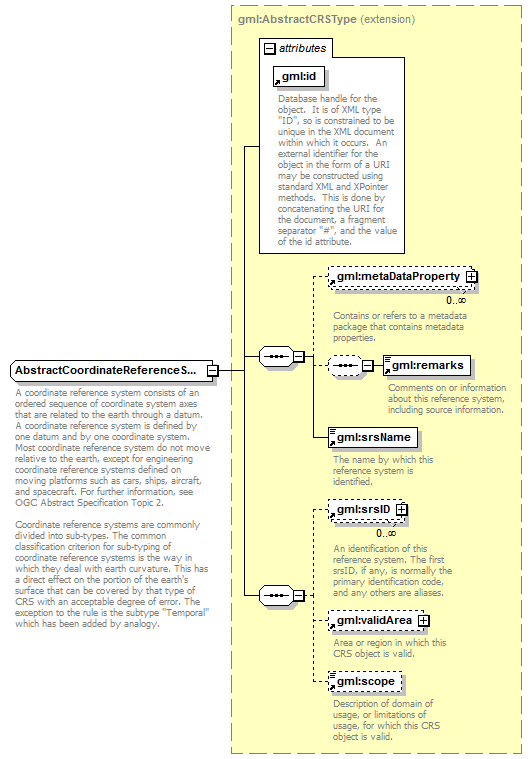
extension of gml:AbstractCRSType |
| properties |
| base | gml:AbstractCRSType | | abstract | true |
|
| children |
gml:metaDataProperty gml:remarks gml:srsName gml:srsID gml:validArea gml:scope |
| used by |
|
| attributes |
| Name | Type | Use | Default | Fixed | Annotation | | gml:id | xs:ID | required | | | | documentation | | Database handle for the object. It is of XML type "ID", so is constrained to be unique in the XML document within which it occurs. An external identifier for the object in the form of a URI may be constructed using standard XML and XPointer methods. This is done by concatenating the URI for the document, a fragment separator "#", and the value of the id attribute. |
|
|
| annotation |
| documentation | A coordinate reference system consists of an ordered sequence of coordinate system axes that are related to the earth through a datum. A coordinate reference system is defined by one datum and by one coordinate system. Most coordinate reference system do not move relative to the earth, except for engineering coordinate reference systems defined on moving platforms such as cars, ships, aircraft, and spacecraft. For further information, see OGC Abstract Specification Topic 2.
Coordinate reference systems are commonly divided into sub-types. The common classification criterion for sub-typing of coordinate reference systems is the way in which they deal with earth curvature. This has a direct effect on the portion of the earth's surface that can be covered by that type of CRS with an acceptable degree of error. The exception to the rule is the subtype "Temporal" which has been added by analogy. |
|
