Enrichment Architecture
The following diagram illustrates the Enrichment architecture.
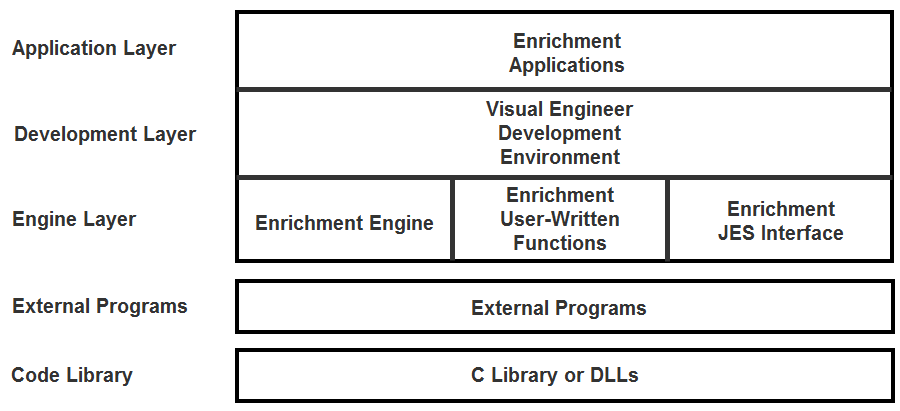
C Library or DLLs
The C library (for mainframe systems or UNIX) or DLLs (for Windows) serve as the code library accessed by the Enrichment engine when running applications. Depending on the platform, various libraries may be required.
External Programs
External programs include presorting, sorting and mail cleansing software called by Enrichment. These programs are not considered part of Enrichment.
Enrichment Engine
The Enrichment engine is the component that processes print streams according to instructions coded in the Enrichment language (control file and rules). The engine runs on a variety of platforms. Code created to run on the engine under one platform will run on all others unless it accesses platform-dependent data, external programs or user-written functions. This book describes coding methods for the Enrichment engine.
Enrichment User-Written Functions
Users can extend Enrichment functionality by writing their own functions in a variety of languages. The object code for the user-written functions must be executable code that has been compiled and linked. On Windows, it may be a DLL.
Enrichment JES Interface
The JES Interface provides the ability for JES spool volume data to be used as input to an Enrichment application. There are two JES interfaces: a non-SAPI interface and a SAPI interface. The non-SAPI interface directly accesses the JES spool volumes. The SAPI interface uses the IBM SYSOUT Application Programming Interface (SAPI) to retrieve spool data, and does not directly access spool volumes.
Enrichment Visual Engineer Development Environment
The Enrichment Visual Engineer development environment is a tool used by developers to build and test Enrichment applications. It runs on Windows and can improve development productivity compared to manually coding and testing applications in a standard editor.
Enrichment Applications
Programmers or printer specialists write Enrichment applications to perform specific functions on specific print files. Each application is coded using the Enrichment language, which includes two basic components:
- Control File: defines the objects to be processed by Enrichment using object-oriented constructs.
- Rule File: defines conditional processing logic for the application in traditional programming code. While a rule file is optional, it is used for most applications. The rule file is composed of sections executed at different points in the application. In many cases the rule file is embedded in the control file so it is not an actual file. However, the rule file can be a separate file that is called from a control file.
Some users build programs that automatically write Enrichment code and generate Enrichment applications.
