|
|
|
Back to |
Selecting fields
Selecting the specific fields that can provide answers to your questions reduces response time and unnecessary records.
Fields represent specific data elements in databases.
InfoSets and SAP Queries
After adding the InfoSet/SAP query into query builder area all the underlying fields in the query are seen in one single table. For each of the fields even the table name is seen.
For InfoSet queries you can choose any field as an output field and they get listed in the criteria pane. You can now set criteria on it. For more details on using the criteria pane, see "Using criteria to define fields".
Notes:
You cannot clear the default selection fields for criteria in an InfoSet. These selection fields have been set during the creation of InfoSets on your SAP server.
You can use only one InfoSet in a query.
For SAP queries, you cannot select or deselect any output or criteria fields.
However, you can modify the criteria. For example, you can change the selection type to Fixed from Runtime, change the Where Clause details, or make the criteria mandatory.
Note: AND expression is not available for SAP queries or InfoSets.
Previewing the query and the number of records to be extracted
- Click Preview run to test the designed query.
- Click Number of entries to see how many records are extracted.
Logical Databases
After the logical database is added to query builder area, select the output fields. The selected output fields appear in the criteria pane.
Note: You can query only one logical database at a time. If you try to add a second LDB to Query Builder, the first selection will be removed as well as any fields that you selected.
Selection fields are the fields on which the criteria is set. You cannot clear any of the existing selection fields or add new selection fields. You can use only what is already set inside the logical database you want to use.
However, you can modify the criteria. For example, you can change the selection type to Fixed from Run time, change the Where Clause details, and make the criteria mandatory.
Note: The AND expression is not available for logical databases on Where clause builder.
In the WHERE clause builder, only those logical operators are available that are applicable to the selected field. For example, if there is a field on the selection screen of an logical database which requires a range of values (such as, FROM and TO) as input, the BETWEEN operator will be available for this field in QUERY.
- Click Preview run to test the designed query.
- Click Number of entries to see how many records are extracted.
Note: The following items are not supported in the current version of QUERY.
- Radio buttons, list boxes, buttons on selection screen
- Logical databases with Dynamic node
- Any logical database which has any additional screen, such as a pop up, which comes after the selection screen
- LDBs Node Types are not supported:
- C - Complex data object
- A – Typed nodes (ANY) at runtime (such as PNP, PNPCE)
Tables
A table can contain from a few fields to hundreds. By default, primary key fields and index fields are listed at the top according to name and description. Fields that are primary keys are represented by a key icon  and index fields are represented by an inverted key icon
and index fields are represented by an inverted key icon ![]() .
.
QUERY also offers other means for you to easily find fields in a table.
To find fields in a specific table
- Right-click the table, and then select one of the following sort or search options on the shortcut menu.
- Sort by name. Sort by ascending or descending order.
- Sort by description. Sort by ascending or descending order.
- Default sorting. By field name, but with primary keys at the top.
- Sort by selection. This option displays your selections at the top of the tables and is useful when you want to create joins between two tables that contain many fields.
- Zoom In on Table. The Fields Selection window shows field names and descriptions. You can search for fields by using a whole name or use the Begin with setting to search by using the first letters of a name.
- Begins with. Select when you are sorting on search fields to search first on field description and then on field name.
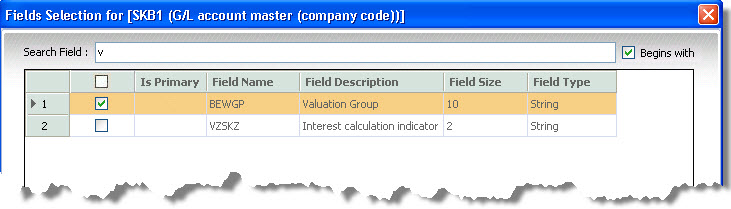
A table after you zoom in. The Begins with setting was selected and the letter v was entered as the search field. It returned two fields whose names and description begin with a "v".
To select fields for output
- Select the check box next to the field you want to add.
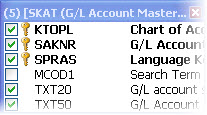
A selected fields in the G/L Account Master table.
To select all fields
- Right-click the table, and then click Select all fields on the shortcut menu.
To deselect all selected fields
- Right-click the table, and then click Deselect all selected fields on the shortcut menu.
Using criteria to define fields
- In the Criteria form, you specify how the fields you have chosen are processed in the query. You also specify criteria that further define the query on the selected fields.
Fields in the criteria pane
Column name |
Details |
Output |
Select this if you want the field to be displayed in the result set. If you clear the check box, you can still use it to build a Where clause and use it to filter data. |
Selection |
Select this if you want to set criteria on a field. |
Field description |
Shows the SAP field description. You can edit it and enter your own custom description. |
Technical name |
The expression table name. Field name is displayed here. |
Selection type |
Using this option you can choose either to predefine the criteria or set it during run time. |
Where clause |
Click the ellipses |
Required |
Select this option to make it mandatory to enter criteria during run time. |
Lookup type |
Select the source for the lookup values. SAP Optional. Either look for values in SAP or manually enter any value. SAP only. Select the values from the list SAP provides. List. Select values from the customized list created by the query designer. |
Padding |
Controls automatic padding for numeric values of string fields. Padding is applied automatically, for Num, Char, Numchar, and string values, but you can select to remove it. Padding improves the accuracy of your data extracts and is important for extracting the correct values from SAP. Note: If you compare non-numeric data without padding, QUERY may return unexpected results. |
SAP type |
The data type of the field in SAP table. |
To add criteria for a field
- Click Selection for the field on which you want to set the criteria.
- The default values for the other columns will appear as explained below
Column name
Default value
Selection type
Runtime
Required
None
Lookup type
SAP optional
- You can change these default values as per your requirements.
- If you chose the Selection type as fixed, the Where clause builder launches as seen in the figure below
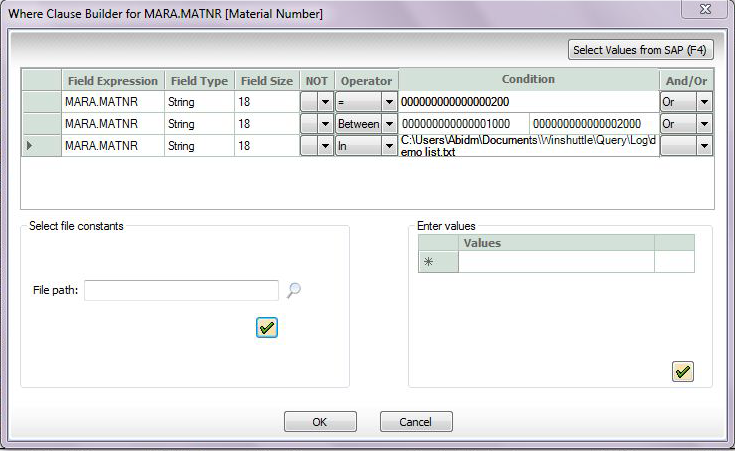
- If you want to make criteria on any field as mandatory, click Required.
- Set the lookup type.
- Click Show Preview to see sample run of the designed query.
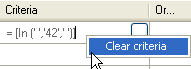
To clear criteria
- Click the criteria that you want to remove, right-click, and then click Clear Criteria.
To sort criteria
- You can sort criteria on the following columns in the criteria pane: Output, Selection, Field Description, and Technical Names.
To reorder rows in the criteria pane
- Drag a row to position you want it to have.
The new order appears in the runtime form and in new queries created in the mapper. You can also open legacy queries and reorder the rows.
The power of WHERE clauses
Use WHERE clauses to limit extractions and thus reduce download time. Where clauses are especially useful in multitable queries. If no WHERE clause is specified, all records will be returned.
With the WHERE clause builder, only those logical operators are available that apply to the selected field. In addition, you can use AND and OR operators between clauses. You can build as many WHERE clauses as you need.
Note that a query line cannot exceed 65,536 characters.
To improve return time for multitable joins, when a criteria is applied to a field in one table, the criteria is also applied to the field in the joined table or tables. Therefore, the join is made only between the filtered records of the tables, not to all the data in the tables.
For InfoSets, the IN operator is now available.

The WHERE Clause builder
Fields in the WHERE clause builder
Field name |
Automatically generated, this indicates the table name and the selected field name. |
Field type |
QUERY displays the type of field, whether a string, double-byte, date or time data type. |
Field size |
QUERY displays the size of the selected field in bytes. |
Padding |
Controls automatic padding for numeric values of the string fields. Note: If you compare non-numeric data without padding, QUERY may return unexpected results. |
NOT operator |
Specify whether you want the inverse (NOT) of the specified operator. |
Operator |
The available operators change according the field that is selected. Operators include =, <, >, <=, >=, <>, Like, Between, In, Is Null, Is not Null |
Condition |
Type a condition to define the search, or press F4 to see a list of SAP values that are allowed for that field. |
OR and And expression |
Use AND or OR to apply more than one condition. |
To specify conditions in a WHERE clause
- Specify an operator or the NOT operator.
- Do one of the following:
- Specify a condition.
- Click inside the Condition box, and then click Select SAP values (F4) to choose a value from SAP.
- Add the list of condition values to a text or Excel file and use Select file constants to indicate the file path.
- Use the Enter values option to enter multiple condition values.
- To apply another condition, click OR or AND, and then repeat steps 1 and 2.
The IN operator
Use the IN operator to check a condition against a list of values.
The IN operator is available for tables and for InfoSets.
- In the Where Clause Builder box, in the Operator column, specify IN.
- Click Text file document or Excel file document.
Tip: To use a column in the current data file for the list of values, click Use result file.
If you are not able to click the options, click inside the Condition column.
- Click the magnifying glass, browse to the file that you want to use, and then click Open.
- Under Excel Values Information, specify the sheet name, column name, and start and end rows.
Note: If the End Row is set to 0, Query will use every row that is in the sheet.
- Click the green check mark to add the file path to the condition.
The following characteristics apply to the IN operator in Winshuttle QUERY:
- A query can contain multiple IN operators.
- Each IN operator may contain no more than 1000 values.
- A query line cannot exceed 65,536 characters.
Output becomes input
For Excel output, the output of a Where clause can become input for the same clause. Using results as input also works well for linked scripts where the first script can become the input for the next script. The output of each script and results can each be written to a different sheet in the same workbook.
To use results as input
- Click New to start a new script and select the data sources you want.
- In the WHERE clause builder, select the field that you want results for.
- For that field, select the IN operator.
- Select Use result file.
- Specify that the results should appear on sheet 2.
- In the Mapper, map the data to an Excel file.
- In the Run pane, click Advanced Run Options, and then link the first script to the second script.
The LIKE operator and wildcards
You can apply wildcards to the LIKE operator to fine-tune your query.
Single underscore or question mark
a_ or a? returns records for values like a1, a2, and ab, but not a12 or abcd. You can use any number of underscores the number of characters you want to match.
Percentage
a% or a* returns all values that start with ‘a’, followed by any number of characters. For example, it matches a1, a2, ab, a12, and abcd.
Select Date Constants/Values
With the Select Constant/Variables option, perform date math, such as Today-120. You can also select the date from the calendar displayed or chose an SAP initialized date. Date values for criteria must always be specified in the correct date format as selected in Tools > Options > SAP Defaults.
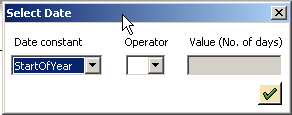
The Enter Values of Run Time Variables dialog box, which appears when you select constants and variables.
Select SAP Values (F4)
To add SAP values to the criteria builder
- To add values appropriate to a field in your criteria builder, click Select SAP Values or press F4.
- Click a value, and then click the Check Mark. The value appears in the Condition box.
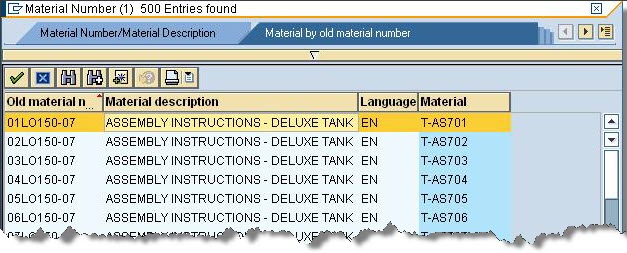
The SAP values that appear when the SAP GUI is available.
- If the SAP GUI is not installed on your computer, or if the field selected in the table has no associated description in SAP, only the values (without their description) are displayed. By default, the first 100 records are scanned and relevant values are displayed. To see more records, specify the number you want to scan in the No. of Records box. Maximum number of values that can be scanned are 5000.
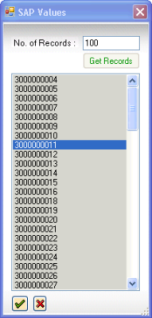
The SAP values dialog box, which appears when you click the SAP Values button.
Adding run time values
When you include run time variables as criteria values, the values must be added at run time. If the criteria was set as "Required", it is mandatory to add values at run time.
If you use the IN operator in the criteria you can select either a text or an Excel file to contain a list of values that are read in when the query is previewed or run.
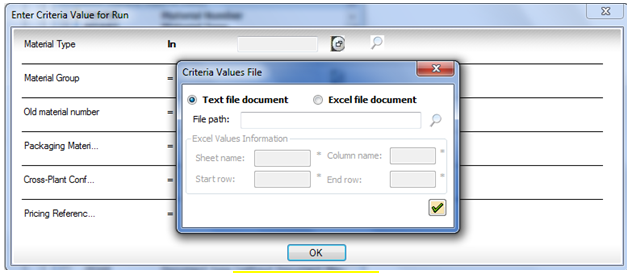
The dialog boxes for the Select File option.
Number of entries
This feature is available for single table and multiple table queries. Click Number of Entries ![]() to see the number of records that the selected criteria will return.
to see the number of records that the selected criteria will return.
Show Preview
- Click the Show Preview button
 to see the kind of records that the query you have built will return. By default, 100 records are returned.
to see the kind of records that the query you have built will return. By default, 100 records are returned.
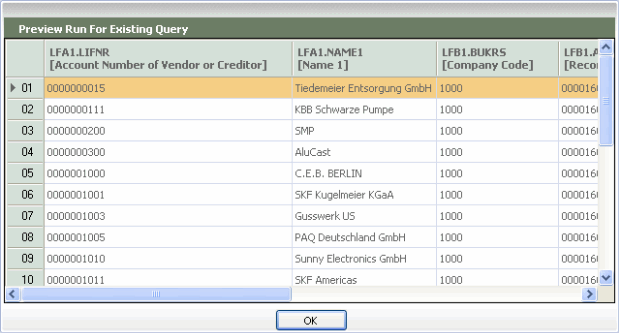
The Preview Run dialog box which displays an example of the kinds of records that will be returned by your query.
Show query
- Click the Show query button
 to see the SQL expression that is created by the query.
to see the SQL expression that is created by the query.
|
Also in this section Tables and the Winshuttle Data Dictionary |

 Home
Home Back
Back Forward
Forward Contents
Contents Index
Index Product Help
Product Help Support
Support Print
Print Feedback
Feedback to launch the Where clause builder and set the criteria.
to launch the Where clause builder and set the criteria. Trademarks
Trademarks Back to top
Back to top


