Archive definitions
Archive is used to generate the appropriate print files (could be PDF) and indices to support writing the output to an archive product. EngageOne™ supports creation of index files for the Vault environment or if you use Generic, for any other vendor’s archive system. Indices are used by the archive system to index the included documents for user search and retrieval. Note that an archive system could support print files, or split PDF files.
If you want to ingest EngageOne™ Interactive documents into EngageOne™ Vault.
To configure archive index specifications:
- Click Delivery Channels.
- Click New.
- Select Type/Archive.
- Select Index.
- Enter the archive file path name using variables as appropriate
- Select Vault or Generic as a File Type. Views will change depending on your selection – see Archive index settings below.
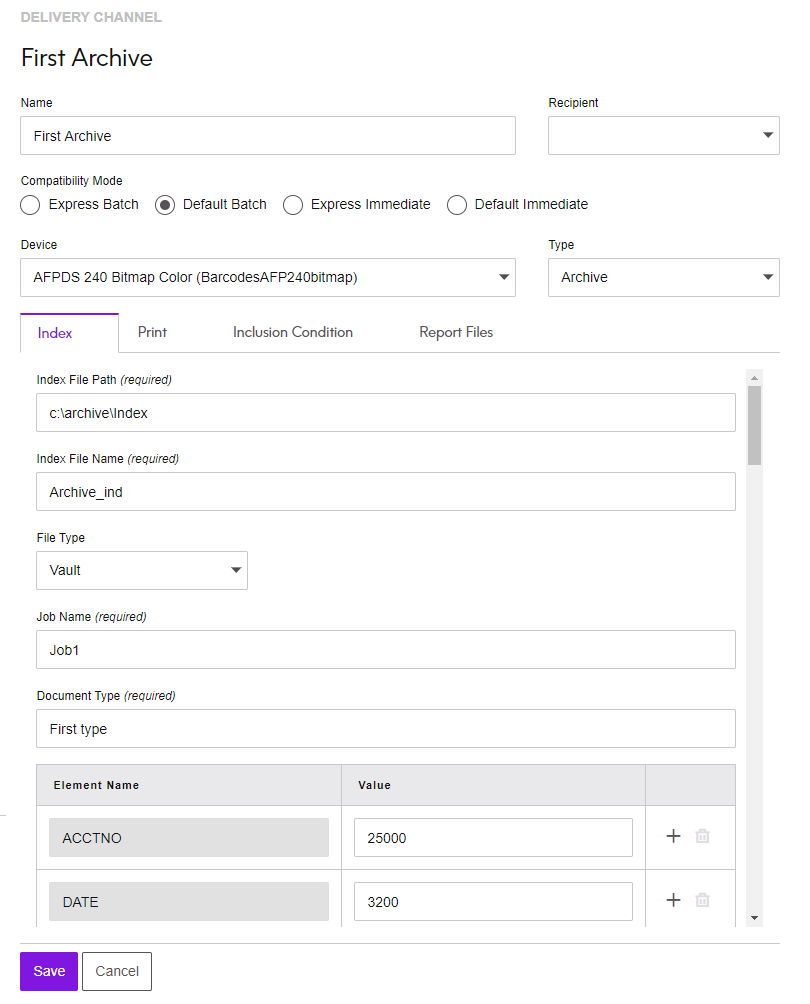
| Archive index file settings | |
|---|---|
| Specific Vault File Type options | |
| Job Name | The name you want to identify the job with. |
| Document type | The name you want to identify the document type with. |
| Element Name / Value | Provide a name and value
pairs, the name being the Element Name and the Value an output variable
or a literal value. You are able to map data to the standard Vault indexes like, account number, date, customer name and address lines. To support custom indexing, you can add any number of element names such as DocID and Iguid with their associated values. |
| Specific
Generic File Type When you specify a Generic file type, this opens further options for recording activity at template, document, or page level as well as at the start and/or end of the job. Note that for an XML report, you specify the root node, which is the wrapper tag, then you specify the node for the report level by clicking the appropriate tab; Template, Document, Page, Job Start, Job End. Then you provide name and value pairs, the name being the element name and the value an output variable or a literal value. |
|
| XML Format options | |
| Root Node | Specify the root node, which is the wrapper tag. |
| Node | Select the level you want
to report on by clicking the required tab; Template, Document, Page, Job Start,
Job End and then specify the appropriate node as per
your selection. Each node is optional, however, if you define a Document or Page node and Template node is empty, you must still define an empty Template node in order for the report output to function correctly. |
| Element Name | Specify the element name. |
| Value | An output variable or a literal value for the report level selected. |
| Delimited Format options | |
| Delimiter | Specify the delimiter. |
| Column | Select the level you want to report on by clicking the required tab; Template, Document, Page, Job Start, Job End and then define the position of the item in the archive file, for the report level selected. |
| Value | An output variable or a literal value for the report level selected. |
| Fixed Width Format options | |
| Column | Select the level you want
to report on by clicking the required tab; Template, Document, Page, Job Start,
Job End and then define the position of the item in
the archive file, for the report level selected. Length – the column length |
| Value | An output variable or a literal value for the report level selected. |
To configure archive print specifications:
- Click Delivery Channels.
- Select Type/Archive.
- Select Print.
- Enter a path name that is appropriate for your server
setup. The path can contain variables and literal values.
– Or
–
right-click on the box for a list of output variables. Click on
the line required and the correct variable syntax will be entered for you.
You may use output variables in a path name but typically it would be combination of literal values and output variables.
Note that you may use output variables in a path name but typically it would be combination of literal values and output variables.
- The File
Name can consist of a combination of literals and output
variables and should include the
INCREMENTsystem variable if partitioning is used. - Enter the File Partition Number if file partitioning should be used. File partitioning is typically used in support of finishing equipment and sets the page count to include in a given print stream (without breaking a document). For example, if you want each output record of the output document to be its own file, then set File Partition Number to 1. If you want the output document partitioned so that there are 100 output records in each file, set File Partition Number to 100.
